
So now onto the glass.
Glass is a tad bit tricky, so this post is a little longer. I'm writing this with the understanding that you want to be a good and better photographer. If you're just shooting every now and then trying to get the kids as they grow up and don't require the better quality, there's no need to read any further. I also write this only touching on the basics of aperture understanding. It would greatly benefit you to research further on this. You can visit the links at the end of this post for starters. In addition, you can always go to
B&C Camera where there are professionals who can answer your questions and help you decide on a lens. If you go to Best Buy or Costco then you are on your own. You've been warned.
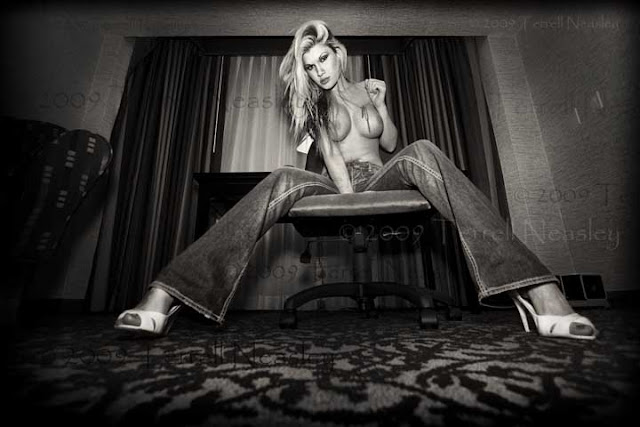 |
| Brie...Shot with a wide-angle lens, distorting perspective especially on the edges |
First... Quite buying cheap glass! That 18-55mm kit lens? Get it off your camera and use it for target practice, especially you Canon shooters. You want to talk about a "starter" lens? Cool. You don't need to spend $2,000 on your first lens. But you do still need to get respectable glass. Notice I said glass. Not plastic lenses, but glass. If you call yourself a pro and I see this in your camera bag, I'm going to talk bad things about you behind your back. Most of the name brand low-end lenses use a plastic barrel and lens. On top of that, they are slow as hell. You ever buy that extra lens, the 55-200mm zoom lens thinking you got a great deal? And then you shoot with it, but can't freeze the action because the camera doesn't take a really quick picture? That's because this lens is slow, but its popular because people don't know any better. The speed of the lens is a factor of how much light it lets in. This is measured by the diameter of the opening, or the aperture as its commonly referred to. Sometimes aperture and the term f/stop are used interchangeably. The maximum aperture of the lens this lens is considered small...too small to let in a lot of light for a quick exposure. More time is required to get enough light in through the smaller opening which means the shutter must stay open longer. So if your subject is being still...great. For moving subjects...not so much. Most zoom lenses have a variable maximum aperture that get's even smaller, and thereby slower the more you zoom out.
Considerations
 |
Shot with a 85mm at f/1.2. Notice how shallow the DofF is?
Basically, from the tip of her nose to her temple. |
In buying a lens, FIRST think about what you are type of photography you are going to shoot. What interests you and what will you spend the majority of your time shooting? This will be the first determining factor in your lens choice. Landscape? Portrait? Sports? Flowers? All these require different lens characteristics. Wide-angle for landscape, Normal lenses for portraits. Fast zoom glass for sports...or really quick kids. And you'll need a macro lens for close-up shots of flowers. But lets say you want to still be a little versatile, despite those specific preferences. A normal lens should then be the first choice with a typical range of 24-70mm, which is the workhorse for most photogs. Or you could go a little longer like the 24-105mm Canon or the 24-120mm Nikon. The 24-70 is usually fast glass at f/2.8. The other mentioned lenses have a maximum aperture of f/4 (slower, but still decent). You can do a lot with these lenses.
The aperture of the lens is the opening in the barrel that lets in light. The smaller the number...the larger the opening. Think of it as a fraction just without the numerator (top number of the fraction). 1/2 is bigger than 1/4, ergo... 2 is bigger than 4. Any lens with a f-stop smaller than f/2.8 is considered slow and like wise f/2.8 and larger is considered fast glass. You want fast glass to learn on because you have more flexibility to experiment. A f/4 lens can do in a pinch at times, but you lose the depth of field option. Any slower lens than that, have your tripods ready.
 |
| *Wikipedia example. As you can see the openings get smaller as you go right. Each next aperture is half the size of the preceding one. F/2.8 lets in double the light as f/4, but only half the light as f/2. (Sizes are not to scale) |
Another thing that is a factor in lenses is Depth of Field. Ever see those shots with the real creamy/blurred background, (referred to as Bokeh) but the subject is tack sharp? And then you wonder why your shots NEVER turn out like that. Chances are its because you have cheap lenses which are slow. Why does that matter? Because Depth of Field is a factor of the aperture setting. The wider the opening, the narrower the depth of field. So larger (hence, faster) apertures will give that effect the wider you open up. Focus on your subject and everything behind goes blurry. The effect is magnified the more open you go beyond 2.8. If you have a lens that opens up to f/1.4, it gets REALLY creamy. Remember...fraction. F/1.4 is opens 2 full stops wider at 4 times the amount of light and thus faster than f/2.8. Conversely, the smaller the aperture, then the longer the depth of field...out to infinity where everything is in focus, including all the foreground and all the background. Depth of Field is extremely important when you shoot portraits.
 |
| Close-up shot with at 100mm f/2.8 with a Macro lens. Also narrow depth of field. |
Primes vs. Zooms. As you probably already realize, zoom lenses start from one point and then "zoom" out to a longer end and you can take a picture at every point within that range. Prime lenses don't have any zoom other than manual. Manual, meaning your feet! You move in or back, manually. These lenses have only one focal length which is the stated focal length on the lens. That's measured in millimeters. 50mm is considered normal, as in what the eye sees. Its often referred to as a STANDARD lens. So basically, your ability to see is derived from the two 50mm eyes you have in your head. Prime lenses are most often considered to be sharper than zooms and that's just because there is less glass and mechanics that light has to travel through to reach the image sensor in the camera. The 50mm with the maximum aperture of 1.8 is the ONLY cheap glass that you can buy and hear nothing from me. These lenses are under $150 and are considered by many to be the best lenses for the value...emphasis on VALUE. However, the 50mm 1.4 is not much more expensive so you may as well get it instead.
 |
Katherine with extended DofF at f/8.
All of background is still in focus. |
Make sure the lens you buy is sturdy, solid, and has a metal mount. The back of the lens where it attaches to the camera should be all metal...not plastic. Say it with me..."NO PLASTIC MOUNTS!" ... Good. Now the next few lines are just suggestions and my professional opinion. Please make up your own minds and do your own research. If I'm not getting a high-end lens, I'm getting a
Tamron. Other popular 3rd party lens manufacturers include, Tokina, and Sigma. I tend to stick with Tamrons if I'm not getting my main manufacturer high-end lens. They simply do the best, IMHO, at providing the better quality at the lower price and better guarantee (6-year warranty). Most of the newer Tamrons have the metal mounts. They have much better build quality than the low end Canons, and are on par with Nikon's low ends. They use mostly glass and have more f/2.8 options on the low end than either major manufacturer. For $500, you can get at least 6 lenses that are 2.8 glass or better. You'll spend more than twice that on 2.8 glass for either Canon or Nikon, (other than the aforementioned 50mm). And if money is no object and you just want the best quality, think
Zeiss...all metal. I mean, everything on this lens is metal except for the high-precision ground, special coated glass lenses. These are manual focus lenses.
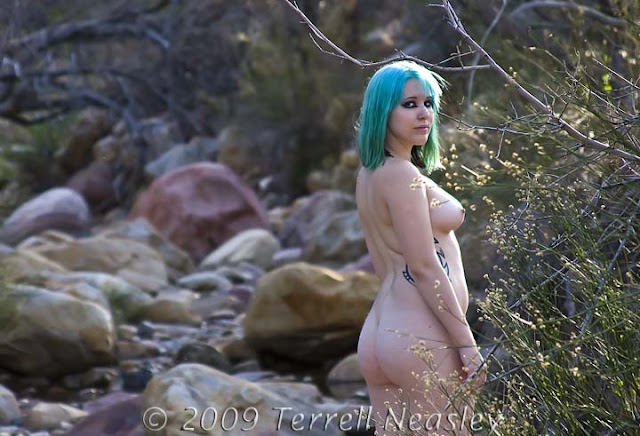 |
| Now this one is tricky. The background is blurry even though the aperture is f/5.6. How is this possible? Because the focal length is in the telephoto range at 135mm! Telephoto lenses "compress" the perspective allowing shorter DofF even at smaller apertures. |
One last consideration is the camera's sensor type. Is it an FX (full frame) or a DX (APS-C cropped sensor)? When you buy a lens for a full frame camera, the focal length is exactly what it says on the lens. If you buy for a DX camera, you have to factor in the camera's multiplier. For Canon, that multiplier is 1.6. For Nikon its 1.5. This means that if the lens says is a 100mm lens, its actually a 160mm lens on a Canon. This is because its thats the Full frame equivalency. A Canon full frame sensor is 1.6 times as large as the DX sensor (see the links below). Some DX lenses won't fit on FX cameras. Canon's won't. Nikon's DX lenses actually do. Tamron lenses also fit on either lens, but be ABSOLUTELY CERTAIN you get the right mount lens when you buy any third part lens. Tamron makes lenses for Canon or Nikon mounts. But if you buy a Tamon with a Nikon mount...it won't fit on a Canon camera. So just make sure that the box says, "FOR CANON" if you have a Canon camera, or "FOR NIKON" if you have a Nikon camera. Make sure the sales person knows which camera you have.
Vibration Control...Image Stabilization...Vibration Reduction...whatever the particular manufacturer calls it, all it means is there is some type of element built into the lens to help reduce camera shake when hand held. So a lens that is considered slow, but has VC may be okay because you can still hand hold it, in some cases this compensation can mean 2 or 3 f/stops slower. I like stabilized lenses and get them over the non-stabilized version when possible, because some lenses will come in two versions: a stabilized version and non-stabilized one. Tamron, as a point of fact, makes the world's only 24-70mm stabilized lens and costs a whole grand less than Canon's.
So start out with the faster glass. You learn better on them because you have more options with speed and depth of field.
If you have a DX camera, here are my top 4 lenses to buy in this order:
1. Either :Tamron 17-50mm f/2.8 with VC (normal lens)
Canon Mount /
Nikon Mount
Or
Tamron 28-75mm f/2.8 designed for full frame but works on DX very well
Canon Mount/
Nikon Mount
(I give the option of the focal range to you. Either one will do. Edge goes to the 28-75mm. Remember the multiplier. The 17-50mm is actually a 25-75mm on a DX camera. The 28-75mm lens is actually a 42-112mm lens on a DX camera. At f/2.8 you'll appreciate the extra reach!)
2. Tamron 10-24 (wide angle)
Canon Mount /
Nikon Mount (with multiplier, its like a 16-35mm lens)
3. Canon or
Nikon 50mm 1.4 (for portraiture. Looks like a 75mm on DX camera)
4. Tamron 70-200mm 2.8 with VC
Canon Mount /
Nikon Mount (looks like a 105-300mm on DX cameras)
If you have a full frame:
1. Tamron 24-70mm 2.8
Canon Mount /
Nikon Mount
2. Canon 16-35mm 2.8/
Nikon 16-35 f/4
3. Canon or
Nikon 70-200mm 2.8 with VC
4. Canon or
Nikon 50mm 1.4
For other interesting lens, look up Tilt-Shift, Fisheye, Teleconverters, Circular Polarizers, Neutral Density Filters, and the fun LensBabies!
Here is some further reading to help you understand:
Canon Full Line-up of Lenses /
Nikon Full Line-up of Lenses
A Tedious Explanation of the f/stop The Long Answer!
Understanding Camera Lenses Cambridge in Color Tutorial
What is a DX Lens? Ken Rockwell covering Nikon DX Lenses
Understanding the Magnification Factor Luminous Landscape
Understanding Depth of Field Cambridge in Color
Understanding Sensor Sizes (DX vs FX, etc)
Next post, I'm going to touch on Light!



















